When Machines Start to “See” the World Intelligently
Have you ever imagined a camera that doesn’t just record, but actually understands what it sees? Computer Vision is when machines begin to “see” the world—not just through lenses, but with intelligence powered by data. Much like a child opening their eyes for the first time, modern cameras now observe, recognize, analyze, and even respond instantly. This capability is being embedded across everyday devices—from smartphones and smart vehicles to public surveillance systems. And the most surprising part? It’s quiet, seamless, and already transforming our daily lives. So what exactly is Computer Vision? How does it work? And why is it becoming so essential in the digital era? Let’s explore together with ATIN.What is Computer Vision?
Computer Vision is a field within Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables machines to “see,” interpret, and understand images or video in a way that mimics human perception. Unlike general AI or machine learning, Computer Vision is focused specifically on visual data:- AI simulates overall human intelligence.
- Machine Learning teaches systems to learn from data.
- Computer Vision uses ML and deep learning to process and understand visual inputs.
- Face recognition for authentication
- Object detection in surveillance
- Self-driving car vision systems
- Barcode or license plate recognition
- Real-time behavior detection in public spaces

How Does Computer Vision Work?
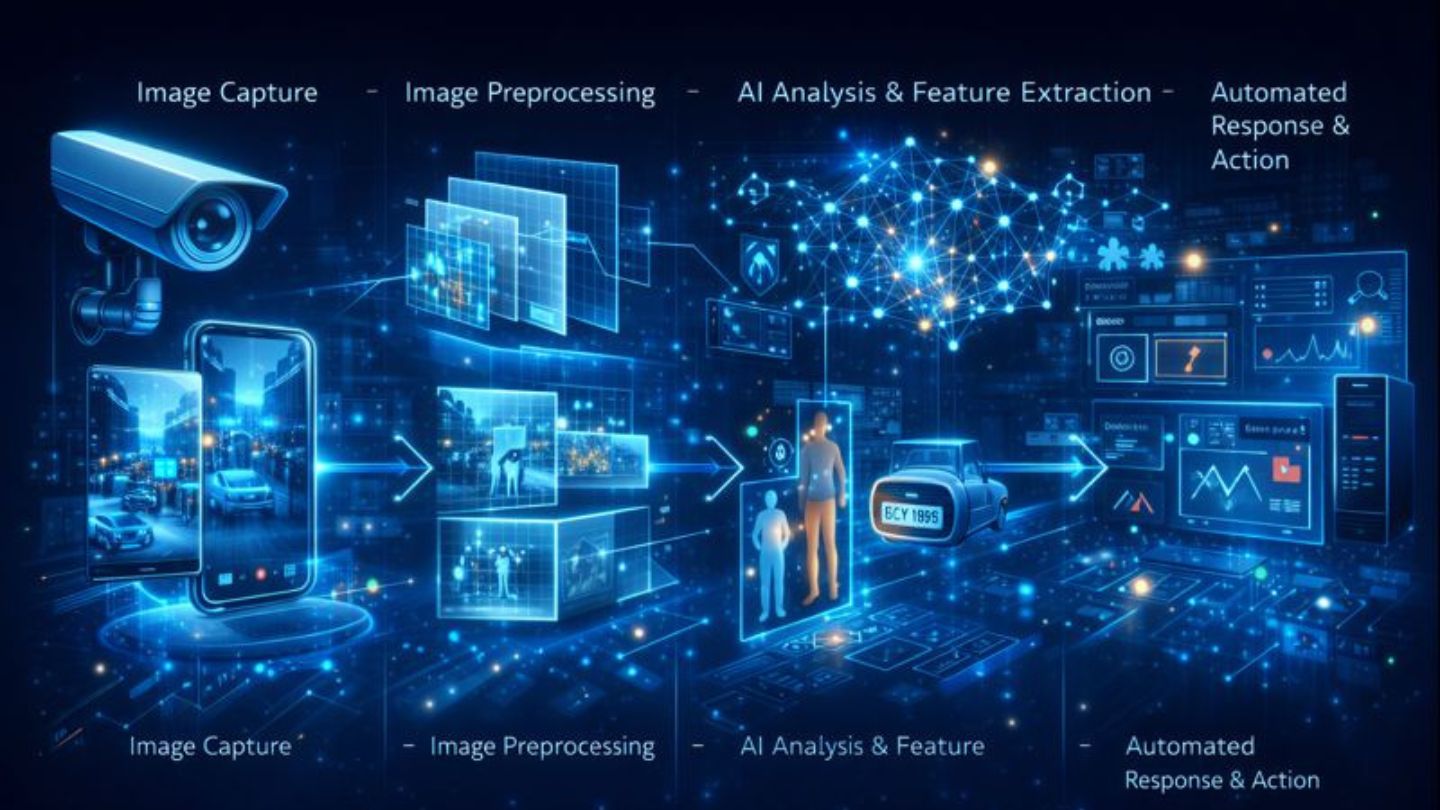
Computer Vision is more than just “seeing”—it’s an intelligent process that interprets visual information and triggers meaningful action. Key steps in Computer Vision include:- Image Capture: Via surveillance cameras, smartphones, scanners, or real-time video streams.
- Image Preprocessing: Enhancing and cleaning the data: adjust lighting, remove blur/noise, normalize size/format, and sometimes convert to grayscale for efficiency.
- Feature Extraction & AI Analysis:
AI models are applied to analyze the images. Common tasks include:
- Object Detection: Identify and locate people, vehicles, or items
- Image Segmentation: Separate objects from backgrounds
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition): Read text from images (e.g., license plates)
- Common frameworks include: YOLO, Mask R-CNN, CRNN, TensorFlow, OpenCV, and PyTorch.
- Automated Response or Action:
Based on analysis, systems can:
- Trigger real-time alerts
- Log access or behavior data
- Count people, vehicles, or detect anomalies
- Feed results into broader analytics systems
Business Benefits of Computer Vision
Adopting Computer Vision leads to measurable improvements across operations:- Increased Productivity: 24/7 surveillance without fatigue — ideal for monitoring factories or logistics operations. Example: A plant in Binh Duong reduced 40% of inspection time with Computer Vision.
- Error Reduction & Real-Time Alerts: Instantly detect product defects, safety violations, or unauthorized access.
- Operational Cost Savings: Many businesses in Vietnam have reduced costs by 20–30% through automation.
Real-World Applications in Vietnam
1. Banking
- Facial recognition at branches
- Real-time fraud detection
- Queue monitoring and customer tracking Example: LPBank uses face-based timekeeping at all branches, replacing card-based systems, reducing fraud, and streamlining reporting.
2. Ports & Logistics
- Vehicle classification
- Container tracking
- License plate recognition Example: ATIN’s Smart Gate at Tan Vu Port (Hai Phong) uses Computer Vision to automate vehicle and container entry. Result: under 30 seconds per vehicle with reduced errors and congestion.
3. Government Facilities
- Access control using facial recognition
- Crowd monitoring in public buildings
- Behavior analytics in large halls or meeting rooms Example: VNPT Smart Vision is deployed across provincial administrative offices to track people flow and detect anomalies in real-time.
4. Healthcare, Factories, and Education
- Contactless temperature checks in hospitals
- Fall detection and patient monitoring
- Defect inspection in production lines
- Face-based attendance in schools
- Classroom behavior analysis

Opportunities & Challenges in Vietnam
Opportunities
- Strong government push for digital transformation
- Affordable AI hardware (cameras, GPUs)
- High demand for process automation
Challenges
- Lack of high-quality image datasets
- Internal resistance due to fear of AI replacing humans
- Integration & maintenance costs
Recommended Approach
- Start small and scale gradually
- Partner with experienced solution providers
- Ensure effective internal communication

