Have you ever wondered why your phone can be unlocked using your face? Or why simply saying “Hey Siri” allows you to check your meeting schedule or set an alarm—without even touching your phone?
What may seem “magical” is actually powered by a technology that has become increasingly present in our daily lives: Artificial Intelligence (AI).
From social media and ride-hailing apps to robotic vacuum cleaners at home, AI is quietly reshaping how we live, work, and connect. But what exactly is AI? How does it work? And will AI replace humans in the future? Let’s explore.
What Is AI?
AI (Artificial Intelligence) refers to the capability of machines to think, learn, and make intelligent decisions in ways similar to humans.
If machines are the body, then AI is the “brain”—programmed to process information, recognize images, understand speech, and even generate creative content. AI is not just a technology; it is a way for machines to perceive and interact with the world.
Everyday examples of AI include:
- Virtual assistants like Siri and Google Assistant
- Video recommendations on TikTok or YouTube
- Smart ride-hailing applications
- Self-driving cars, robotic vacuum cleaners, smart security cameras

How Does AI Work?
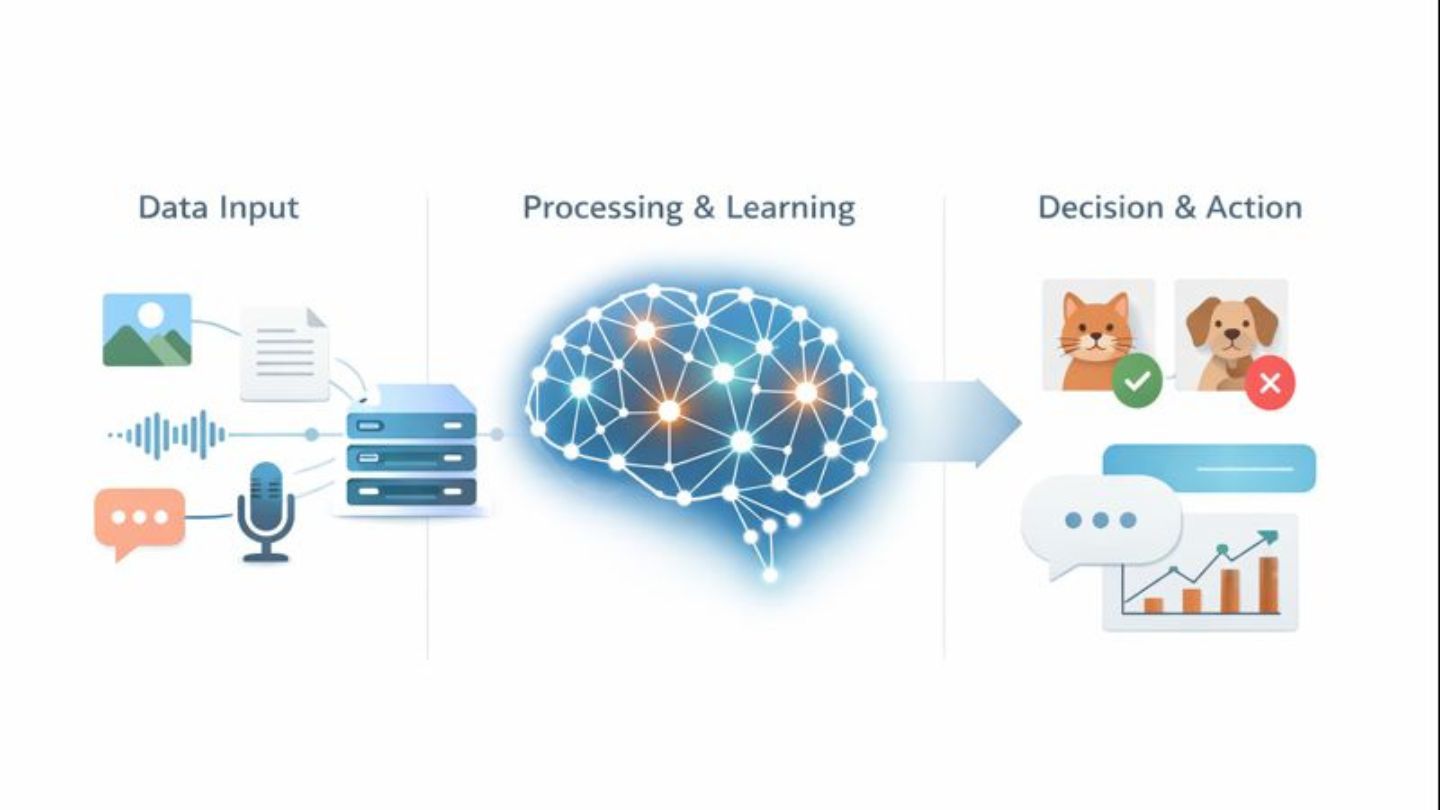
Simply put, AI operates through three main steps:
- Data input: Images, audio, text, and more
- Processing and learning: Using algorithms—especially Machine Learning and Deep Learning
- Decision-making or action: Such as image classification, message responses, or predictions
A simple example:
AI learns to distinguish between cats and dogs by “looking at” thousands of labeled images. Over time, it recognizes patterns and differences—much like how a child learns from real-world experience.
Will AI Replace Humans?
This is one of the most frequently asked questions about AI.
The answer is: Not yet—and likely not completely.
AI excels at:
- Processing large volumes of data quickly
- Performing repetitive tasks
- Delivering accurate analysis and statistics
However, AI still cannot replace human emotions, creativity, flexibility, and—most importantly—empathy.
For example:
- AI can analyze lung scans, but doctors understand a patient’s emotions and personal context.
- Chatbots can answer questions, but teachers inspire curiosity and motivation in students.
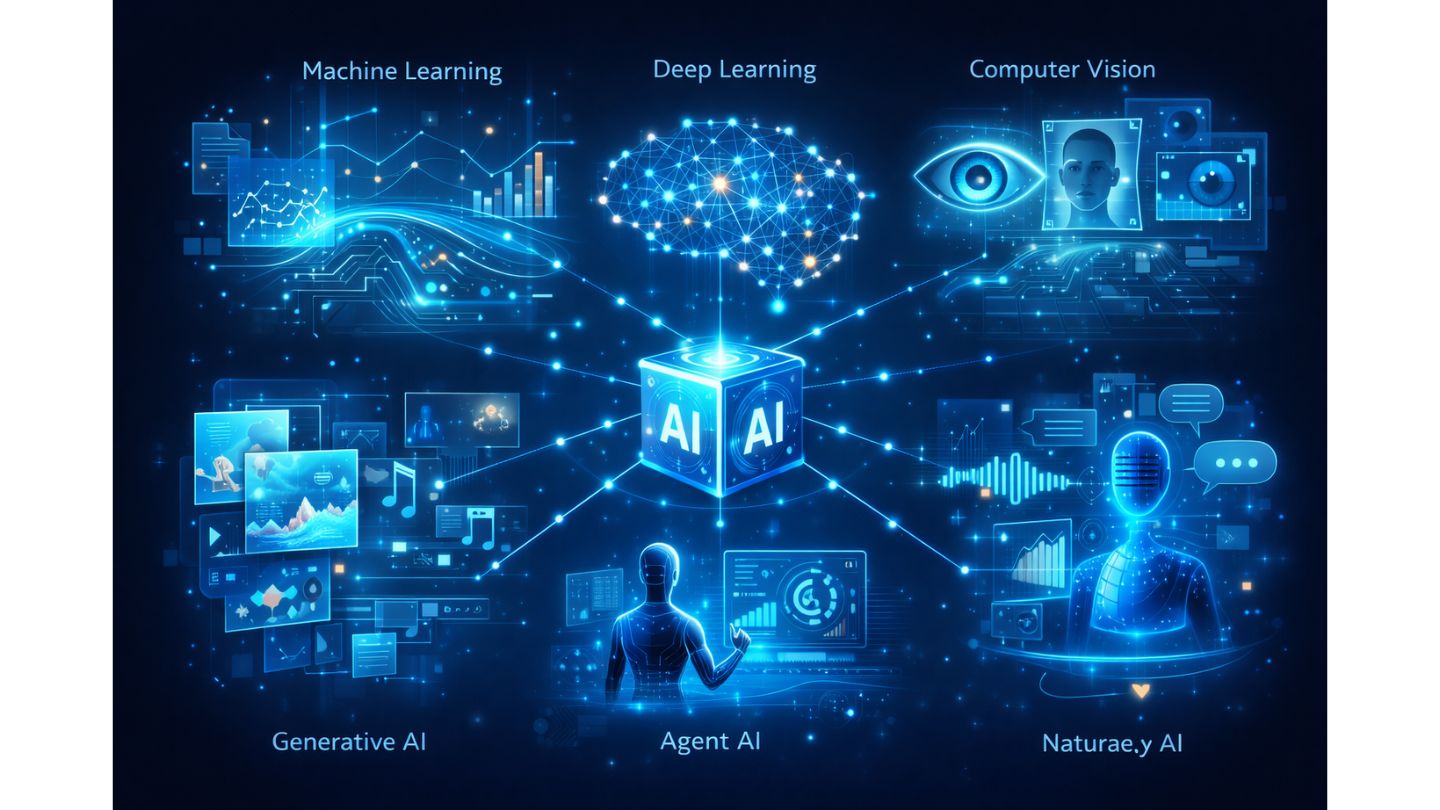
Popular AI Technologies Today
AI is a broad field developed through multiple approaches, each serving a distinct purpose—from helping machines “see” and “hear” to enabling autonomous decision-making.
Key AI technologies include:
- Machine Learning: The foundation of most AI systems, allowing machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed for every scenario.
- Deep Learning: An advanced branch of machine learning that uses multi-layer neural networks to process complex data such as images and speech.
- Computer Vision: Enables machines to interpret images and videos—used in facial recognition, license plate detection, and security monitoring.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allows machines to understand and respond to human language, used in chatbots, translation, and text summarization.
- Generative AI: Enables machines to create new content such as text, images, or music—examples include ChatGPT and Midjourney.
- Agent AI: AI systems capable of making decisions and acting independently based on defined goals and environments, often used for virtual assistants and enterprise automation.
Opportunities and Challenges of AI
Opportunities
Boost productivity and efficiency
AI can complete tasks in minutes that would take humans hours or days—such as sorting emails, screening job applications, or detecting coding errors—freeing people to focus on creative work.
Reduce operational costs
AI-powered automation lowers labor costs for repetitive tasks. Many businesses use chatbots for 24/7 customer support or AI analytics instead of large analysis teams.
Create new careers
AI development has given rise to new roles such as AI Trainer, Data Engineer, and AI Ethicist—highly sought-after positions in today’s job market.
Challenges
Job displacement concerns
Repetitive roles such as data entry, inspection, or driving may be partially replaced by AI, requiring workers to continuously reskill and adapt.
Ethics and privacy issues
As AI collects and analyzes personal data, concerns around privacy and security grow—especially with facial recognition systems if not properly regulated.
Over-reliance on technology
Excessive dependence on AI for decision-making can reduce human judgment and response capability, reinforcing the need for human oversight and critical thinking.
A Trusted Partner, Not a Replacement
Rather than fearing replacement, we should see AI as a reliable partner—one that supports human work when used responsibly and collaboratively.
“Understanding AI So You’re Not Left Behind”
AI is no longer science fiction. It already exists in everyday moments—when you search for directions, send voice messages, or receive calendar reminders. It’s in your workplace, your home, and even in systems supporting doctors in hospitals.
When you understand what AI is, how it works, and its real limitations, you gain confidence. Instead of feeling overwhelmed by change, you become proactive—choosing how to engage with technology on your own terms.
At that point, the question is no longer “What is AI?”
It becomes:
How can I use AI in the smartest and most meaningful way for myself?

