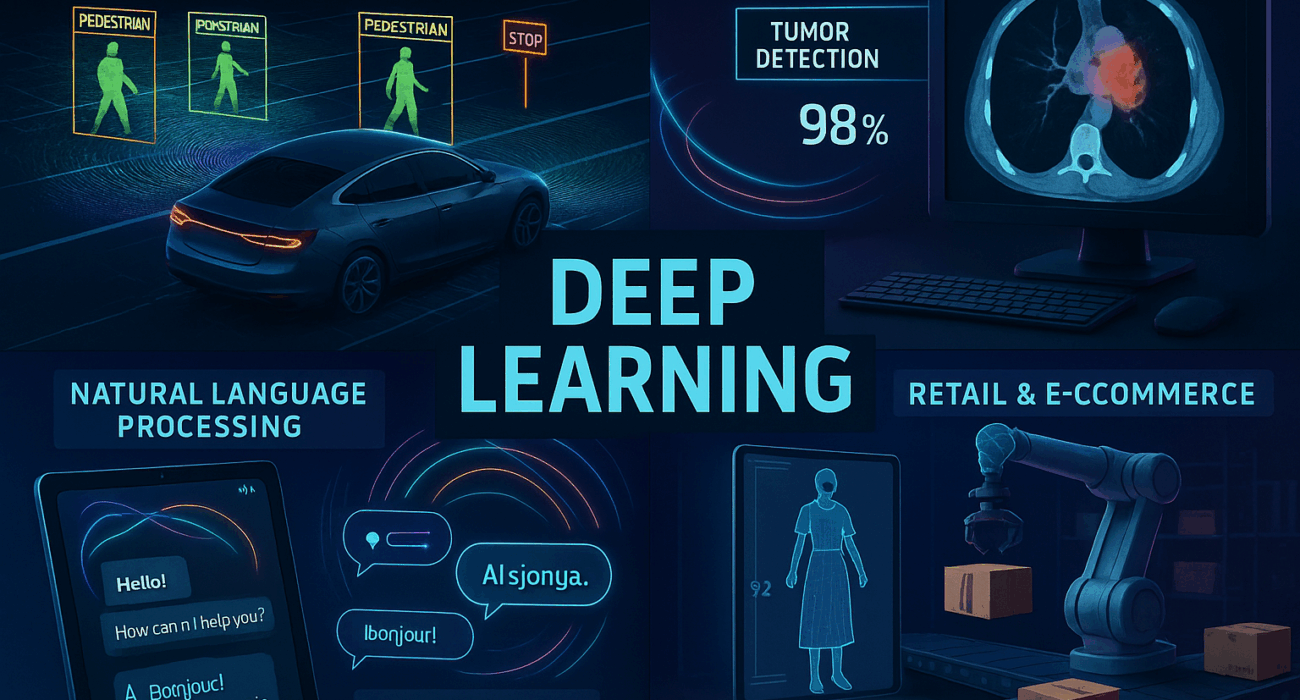
Deep Learning là một nhánh tiên tiến của trí tuệ nhân tạo, giúp máy móc “học” và “suy nghĩ” giống con người. Từ hệ thống nhận diện khuôn mặt đến xe tự lái hay phân tích ảnh y tế – tất cả đều là ứng dụng của Deep Learning. Nhưng công nghệ này có gì đặc biệt? Và liệu doanh nghiệp Việt Nam đã sẵn sàng tận dụng nó?
Deep Learning là gì?
Deep Learning (học sâu) là một phương pháp thuộc trí tuệ nhân tạo (AI), trong đó máy tính học từ dữ liệu bằng cách sử dụng các mô hình gọi là mạng nơ-ron nhân tạo. Nó mô phỏng cách bộ não con người hoạt động – học từ kinh nghiệm, nhận diện mẫu, và tự cải thiện sau mỗi lần lặp.
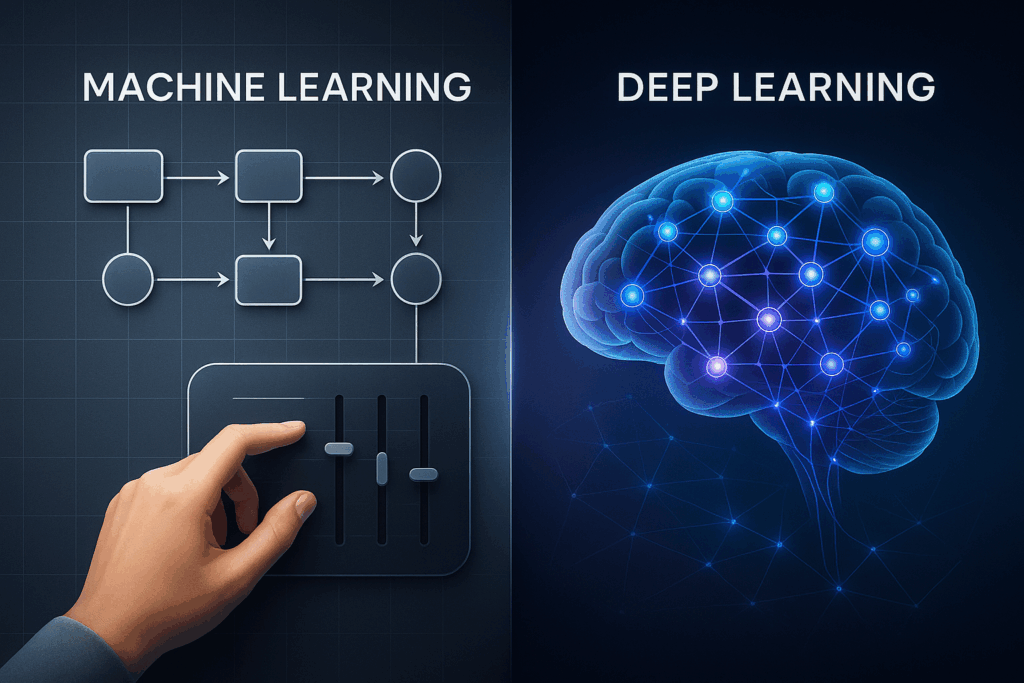
So với Machine Learning, Deep Learning có gì khác?
- Machine Learning cần con người can thiệp vào bước chọn đặc trưng dữ liệu.
- Deep Learning học đặc trưng từ dữ liệu thô mà không cần lập trình cụ thể.
Ví dụ: Trong nhận diện hình ảnh, Machine Learning cần bạn chọn các điểm nổi bật (mắt, mũi, miệng), còn Deep Learning tự học được những yếu tố này.
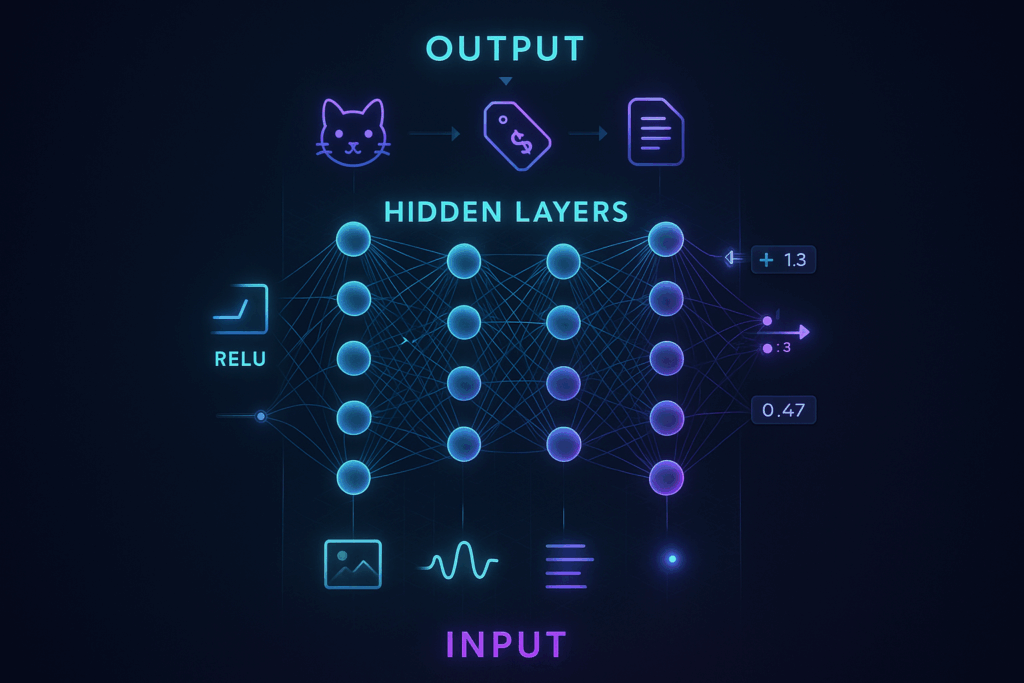
Deep Learning hoạt động như thế nào?
Deep Learning hoạt động dựa trên một kiến trúc gọi là mạng nơ-ron nhân tạo sâu (deep neural network), gồm nhiều tầng (layers) mô phỏng cách con người xử lý thông tin.
Các tầng trong mạng nơ-ron hoạt động ra sao?
Một mô hình Deep Learning thường có 3 loại tầng chính:
- Tầng đầu vào (input layer):
Nhận dữ liệu thô từ thực tế như ảnh, âm thanh, văn bản… Ví dụ, nếu đầu vào là ảnh 28×28 pixel, tầng này sẽ có 784 nút (neuron), mỗi nút đại diện cho giá trị của 1 pixel. - Tầng ẩn (hidden layers):
Đây là trái tim của mạng, nơi mọi “ma thuật” xảy ra. Mỗi tầng ẩn sẽ:- Nhận thông tin từ tầng trước.
- Áp dụng trọng số (weights) và độ lệch (bias).
- Kích hoạt thông qua một hàm phi tuyến (activation function) như ReLU hoặc Sigmoid.
- Truyền kết quả cho tầng tiếp theo.
- Tầng đầu ra (output layer):
Đưa ra kết quả cuối cùng như phân loại (mèo hay chó), dự đoán (giá nhà), hay tạo văn bản mới.
Mỗi liên kết giữa các neuron giống như một “đường dẫn thông tin”, và trọng số giống như “độ quan trọng” của thông tin đó. Mạng học bằng cách điều chỉnh các trọng số này để giảm sai số.
Quá trình học của Deep Learning: từ dữ liệu đến thông minh
- Forward Propagation (Lan truyền xuôi):
Dữ liệu đi từ đầu vào đến đầu ra qua từng tầng. Mỗi bước là một phép toán tuyến tính (ma trận × vector), kết hợp với hàm phi tuyến. - Tính sai số (loss):
So sánh đầu ra mô hình với kết quả thật. Ví dụ, ảnh là “mèo” nhưng mô hình dự đoán “chó” → sai số cao. - Backward Propagation (Lan truyền ngược):
Mạng dùng đạo hàm và chuỗi đạo hàm (chain rule) để tính xem mỗi trọng số đã gây ra sai số bao nhiêu. - Cập nhật trọng số (học):
Sử dụng thuật toán tối ưu (như Gradient Descent) để điều chỉnh trọng số sao cho sai số nhỏ dần theo thời gian.
Quá trình này lặp lại hàng nghìn hoặc hàng triệu lần cho đến khi mô hình đủ chính xác.
Ví dụ: Giống như khi bạn dạy một đứa trẻ phân biệt chó và mèo. Ban đầu, trẻ phân biệt sai. Nhưng sau nhiều lần chỉ dẫn và thử lại, trẻ dần học đúng. Mạng nơ-ron hoạt động tương tự.
Vì sao Deep Learning bùng nổ thời gian gần đây?
Sự phát triển nhanh của Deep Learning đến từ ba yếu tố chính:
- Dữ liệu lớn (Big Data): Các doanh nghiệp tạo ra lượng dữ liệu khổng lồ mỗi ngày.
- Sức mạnh tính toán tăng: GPU và chip AI giúp mô hình học nhanh hơn.
- Framework mã nguồn mở: TensorFlow, PyTorch giúp các nhóm nhỏ cũng có thể thử nghiệm dễ dàng.
1. Dữ liệu lớn (Big Data)
Hiện nay, doanh nghiệp thu thập dữ liệu với tốc độ chưa từng có. Từ video giám sát, cảm biến IoT đến giao dịch khách hàng – dữ liệu ngày càng phong phú. Nhờ đó, Deep Learning có cơ hội “học” sâu hơn từ nguồn thông tin thô chưa xử lý. Khác với phương pháp truyền thống, Deep Learning tự tìm ra đặc trưng ẩn bên trong dữ liệu. Do vậy, càng có nhiều dữ liệu, mô hình càng thông minh và chính xác hơn.
2. Sức mạnh tính toán vượt trội
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) không chỉ phục vụ game mà còn là “bộ tăng áp” cho AI. Nhờ khả năng xử lý hàng ngàn phép toán song song, GPU giúp Deep Learning huấn luyện nhanh hơn hàng chục đến hàng trăm lần so với CPU . Điều này khiến các mô hình lớn – như nhận dạng ảnh hoặc xử lý ngôn ngữ – trở nên khả thi trên quy mô doanh nghiệp.
3. Framework mã nguồn mở tiên tiến
TensorFlow, PyTorch, MXNet… không chỉ miễn phí, dễ tiếp cận mà còn tối ưu cho xây dựng mạng nơ‑ron sâu và huấn luyện trên đa GPU/máy. Nhờ vậy, các tổ chức từ startup đến đại học đều có thể thử nghiệm, triển khai và tối ưu Deep Learning mà không phải “đi lối tắt” .
Hiệu quả ứng dụng thực tế
Theo McKinsey, doanh nghiệp triển khai AI (bao gồm Deep Learning) đã cải thiện hiệu suất từ 20% đến 30% trong các lĩnh vực như vận hành, marketing và ra quyết định. Chẳng hạn, AI giúp tối ưu tồn kho, dự đoán nhu cầu, tiết kiệm chi phí và tăng năng suất rõ rệt. (Nguồn: McKinsey)
Ứng dụng Deep Learning tại Việt Nam
1. Ngân hàng
- Nhận diện khuôn mặt để xác thực & chấm công
Từ đầu 2024, Ngân hàng Nhà nước đã yêu cầu áp dụng xác thực sinh trắc học (face ID) cho mọi giao dịch trên nền tảng số từ 10 triệu đồng (~ $390) trở lên. (Nguồn: Báo điện tử chính phủ)
Một số ngân hàng nội địa như Techcombank và Vietcombank đã phát triển hệ thống xác thực bằng khuôn mặt do kỹ sư Việt Nam thiết kế, giúp đẩy mạnh bảo mật và nâng cao trải nghiệm khách hàng . - Phát hiện gian lận qua hành vi & giao dịch
Các tổ chức như Feedzai hợp tác với ngân hàng Việt để triển khai biometric + phân tích hành vi giao dịch nhằm phát hiện deepfake, spoofing hay tài khoản bị chiếm quyền. (Nguồn: Feedzai)
Kết quả? Rủi ro gian lận giảm đáng kể, tiết kiệm chi phí giám sát và cải thiện niềm tin khách hàng.
2. Y tế
- Phân tích ảnh X-quang, CT bằng Deep Learning
VinBigData (thuộc Vingroup) phát triển hệ thống VinDr – cho chẩn đoán ung thư vú, phổi, viêm phế quản trên ảnh X-quang/CT, được thử nghiệm tại các bệnh viện lớn như 108, Vinmec, Đại học Y Hà Nội. (Nguồn: National Library of Medicine)
VenBrain – qua nền tảng DrAid, đã triển khai tại 63 cơ sở y tế ở Việt Nam, giúp bác sĩ chẩn đoán nhanh hơn đến 80% nhờ GPU NVIDIA DGX A100. - AI phát hiện lao phổi (TB)
Nghiên cứu tại Bệnh viện Phổi Trung ương phối hợp với viện công nghệ Việt Nam phát triển mô hình CNN phân tích X-quang phổi người Việt, đạt độ nhạy đặc hiệu trên 90%. Chưa kể, VinBrain cũng tích hợp thêm khả năng chẩn đoán lao vào DrAid. (Nguồn: AuntMinnieEurope)
3. Logistics – kho vận
- Giám sát tự động & dự báo tắc nghẽn
Báo cáo từ International Journal of Scientific Research & Management chỉ ra rằng deep learning giúp công ty logistics ở Việt Nam cải thiện dự báo nhu cầu, tối ưu giao hàng và giảm chi phí. (Nguồn: ResearchGate)
Họ triển khai camera AI trong kho để tự động phát hiện kiện hàng lỗi và theo dõi tình trạng lưu kho. Mô hình còn dự báo tắc nghẽn theo thời gian thực, giúp tối ưu tuyến vận chuyển.
4. Giáo dục – trường học
- Nhận diện khuôn mặt, phân tích hành vi học sinh
Nhiều trường học tại Hà Nội và TP.HCM đã thử nghiệm hệ thống điểm danh tự động bằng camera AI.
Học sinh đi muộn, vắng mặt được cập nhật ngay vào hệ thống điểm danh điện tử. Bộ phận IT có thể theo dõi hành vi: chép bài, tương tác trong giờ, giúp phát hiện học sinh cần hỗ trợ.
>Một nghiên cứu từ MDPI năm 2025 so sánh hiệu quả phân loại tín dụng (student credit scoring) giữa ML và Deep Learning dùng tại các tổ chức giáo dục Việt Nam – cho thấy deep learning hiệu quả hơn rõ rệt. (Nguồn: mdpi.com)
Tương lai Deep Learning tại Việt Nam
Deep Learning đang dần trở thành công nghệ thiết yếu mà không còn là điều gì đó quá xa vời. Các doanh nghiệp Việt Nam đang chuyển dịch mạnh mẽ sang tự động hóa và ra quyết định bằng dữ liệu.
Theo TopDev 2024, nhu cầu tuyển dụng kỹ sư AI tăng 45% mỗi năm tại Việt Nam. Không chỉ ngành công nghệ, mà ngân hàng, sản xuất, giáo dục cũng đang cần nhân lực AI gấp.
VietnamWorks cho biết: kỹ sư Deep Learning có thu nhập trung bình hơn 2.000 USD mỗi tháng. Điều này phản ánh rõ xu hướng đầu tư mạnh vào AI của các doanh nghiệp trong nước.
Ba tín hiệu rõ ràng cho thấy Deep Learning sẽ thành tiêu chuẩn:
- Người dùng đòi hỏi trải nghiệm nhanh, cá nhân hoá và không bị lặp lại.
- Chính phủ Việt Nam đặt mục tiêu AI trong top 4 ASEAN đến năm 2030.
- Doanh nghiệp không áp dụng AI sẽ tốn nhân lực, vận hành kém và tụt hậu.
Khi Deep Learning trở thành tiêu chuẩn mới
Deep Learning đang từ “ưu thế” trở thành “bắt buộc” trong nhiều lĩnh vực vận hành. Giống như doanh nghiệp nào cũng cần website sau 2010. Giống như CRM là yêu cầu tối thiểu sau 2020.
Thì đến 2027, AI sẽ là tiêu chuẩn mặc định cho mọi doanh nghiệp. Nếu không có, doanh nghiệp sẽ đi chậm hơn thị trường.
Giờ là lúc hành động
Bạn không cần chờ có đội ngũ kỹ thuật để triển khai Deep Learning. Nhiều giải pháp đã có sẵn dưới dạng mô-đun hoặc tích hợp. Doanh nghiệp vừa và nhỏ vẫn có thể bắt đầu từng bước phù hợp. Ứng dụng sớm, bạn sẽ đi trước đối thủ một bước trong chuyển đổi số.
Đừng để đối thủ vượt mặt bằng công nghệ.
Hãy trở thành người dẫn đầu trong ngành của bạn.
Liên hệ với chúng tôi ngay để được tư vấn ứng dụng AI hoàn toàn miễn phí.